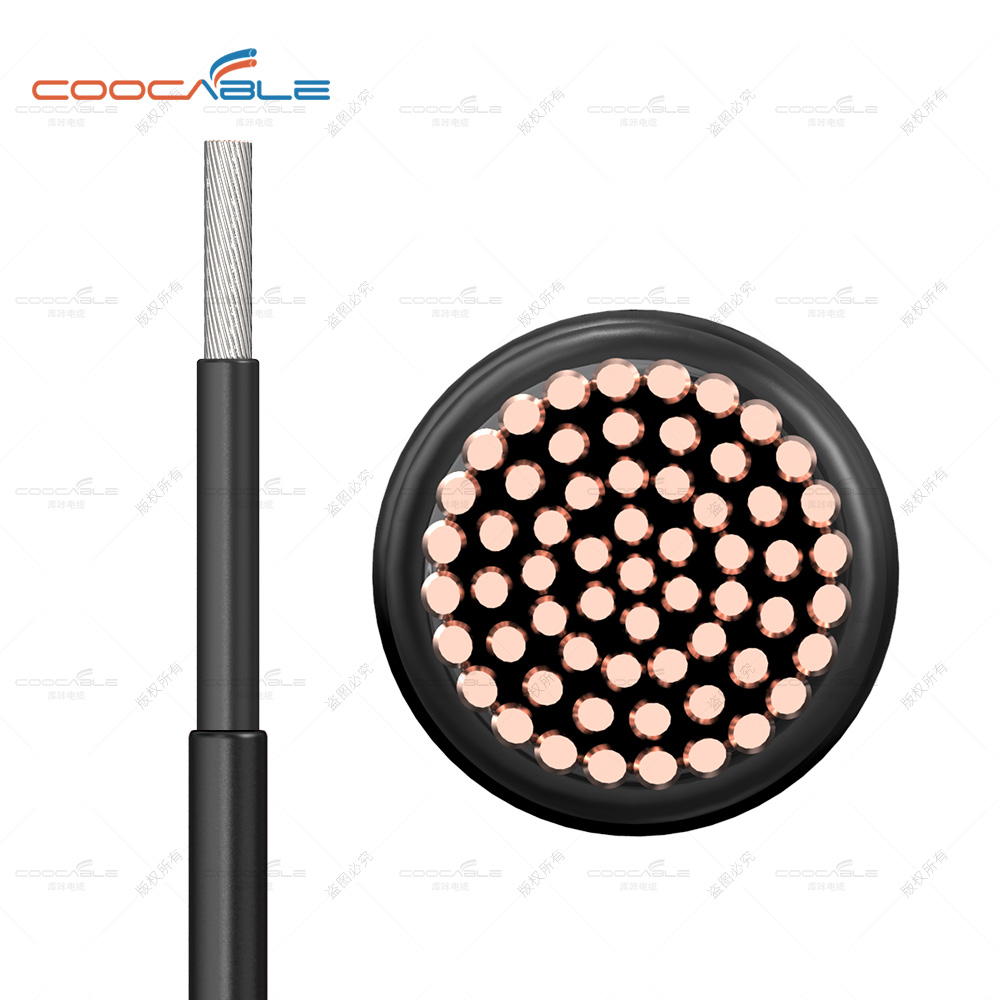
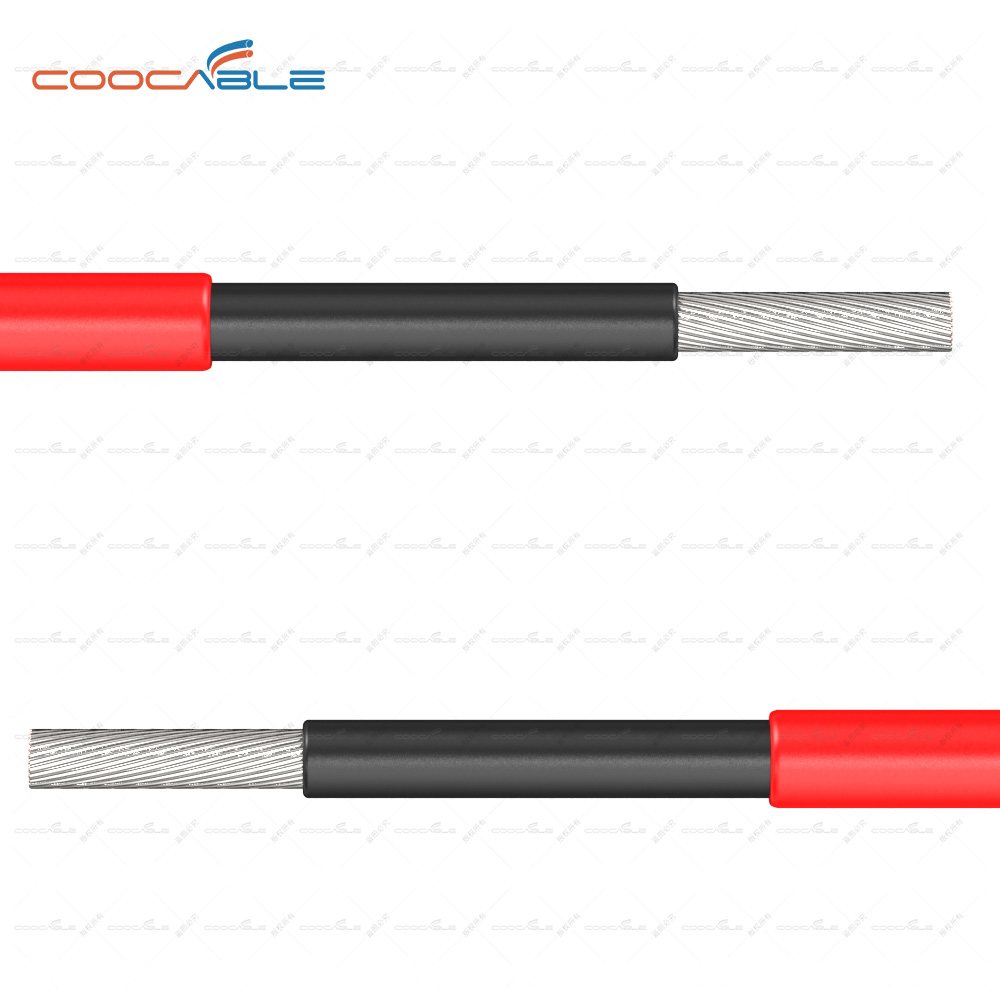
The difference between solar cables and ordinary cables is as follows
Photovoltaic cables, also known as solar photovoltaic cables, have specialized types such as PV1-F and H1Z2Z2-K. Let's compare photovoltaic cables and ordinary electrical cables in terms of conductor, insulation, jacket, and application scenarios, and analyze the differences between them.
[Conductor]
Photovoltaic cables: Copper conductor or tinned copper conductor
Ordinary electrical cables: Copper conductor or tinned copper conductor
[Insulation]
Photovoltaic cables: Cross-linked polyolefin insulation
Ordinary electrical cables: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or cross-linked polyethylene insulation
[Jacket]
Photovoltaic cables: Cross-linked polyolefin insulation
Ordinary electrical cables: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) jacket
From the above information, we can see that photovoltaic cables and ordinary electrical cables have the same conductor, while their differences lie in the insulation and jacket materials.
[Cross-linked Polyolefin] Cross-linked polyolefin has strong environmental adaptability, resistance to chemical corrosion, creep resistance, and high temperature resistance, with a maximum rated temperature of up to 125°C.
[Polyvinyl Chloride] PVC has the advantages of stable structure, high resistance to chemical agents, good mechanical strength, and insulation properties. However, PVC has poor stability to light and heat, with a maximum rated temperature of 55°C.
[Cross-linked Polyethylene] It has a cross-linked structure, excellent heat resistance, and higher insulation performance than PE materials. It exhibits improved hardness, rigidity, wear resistance, and impact resistance. It has strong chemical resistance, including resistance to acids, alkalis, and oils. The maximum rated temperature is 90°C.
Due to the specific requirements of photovoltaic power systems, photovoltaic cables need to possess special characteristics such as weather resistance, high temperature resistance, friction resistance, resistance to UV exposure, ozone resistance, hydrolysis resistance, acid resistance, and salt resistance. Cross-linked polyolefin insulation meets these requirements. PVC or cross-linked polyethylene insulation has slightly lower heat resistance compared to cross-linked polyolefin insulation, which is why ordinary electrical cables cannot be used in photovoltaic applications.