What you should know about medium voltage cables
What you should know about medium voltage cables
product description
Power cables can be divided into medium and low voltage power cables (35 kV and below), high voltage cables (above 110 kV), ultra-high voltage cables (275-800 kV), and UHV cables (1000 kV and above) according to to their voltage levels. ).
The voltage range of medium voltage cables is between 6KV and 33KV, and copper and aluminum are the main conductor materials. Copper is more common in medium-voltage cable designs, while aluminum is more commonly used in high-voltage cables.
Product Standards
IEC 60502-2 is the worldwide standard for medium voltage cables. It covers cables with rated voltages up to 36 kV. It also includes armored cables, as well as single-core and multi-core cables. Two other standards for medium voltage cables are IEC/EN 60754 and EN 60332, which evaluate the content of halogen acid gases and measure the flame spread in the event of a fire. These two standards also specify smoke-intensive tests for cables that burn under specific conditions
Scope of application
In industrial environments, medium-voltage power cables are mainly used in power distribution systems. They can be installed in pipes or conduits and are suitable for wet and dry locations. Typical applications include pulp and paper mills, petrochemical plants, water treatment plants, environmental protection systems, and railways. UV-resistant medium voltage cables for distribution networks and connections to generator sets and plant and process connections. Due to their robustness and high electrical stability, medium-voltage cables are used in harsh environments. They are available in a variety of structures and armor
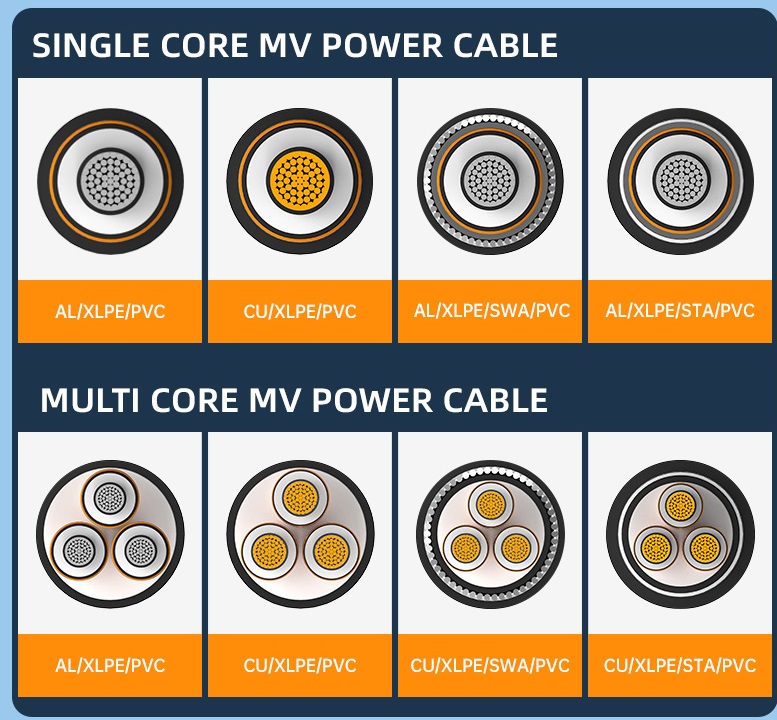
Product Category
Product parameters
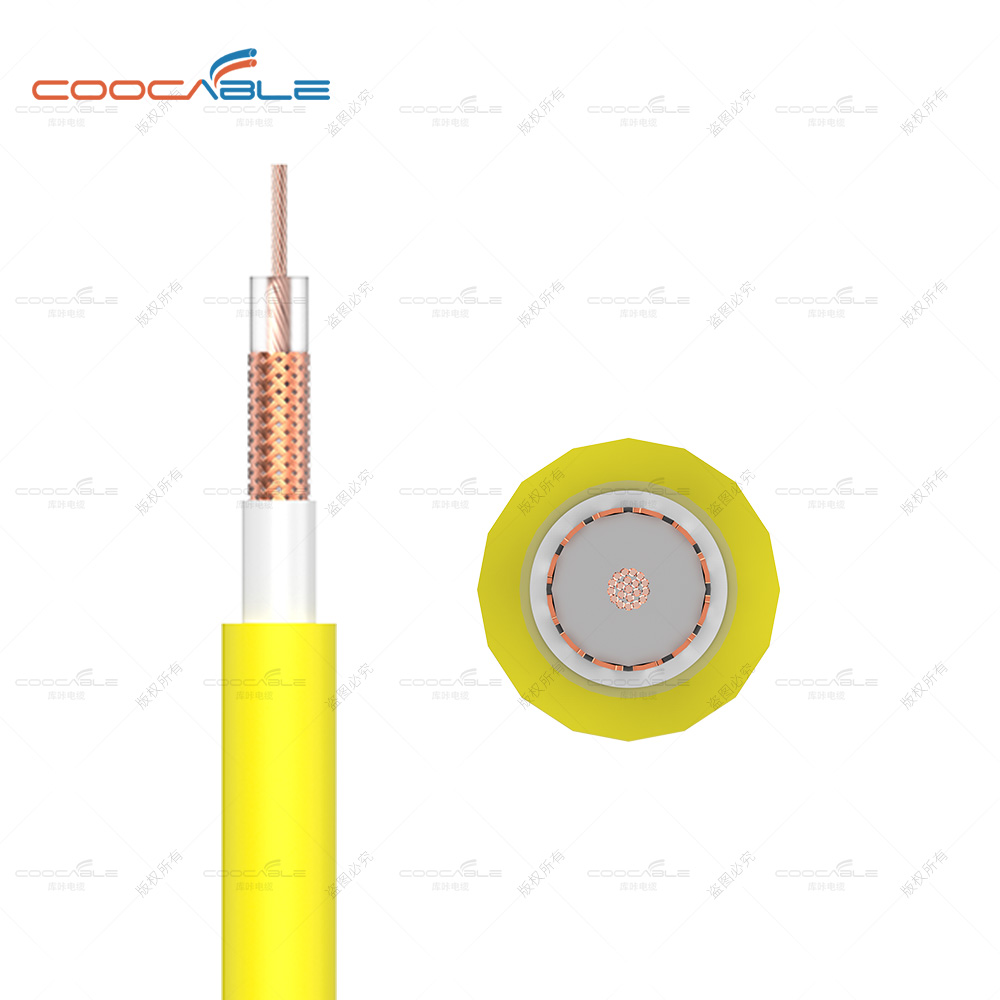
CONSTRUCTION
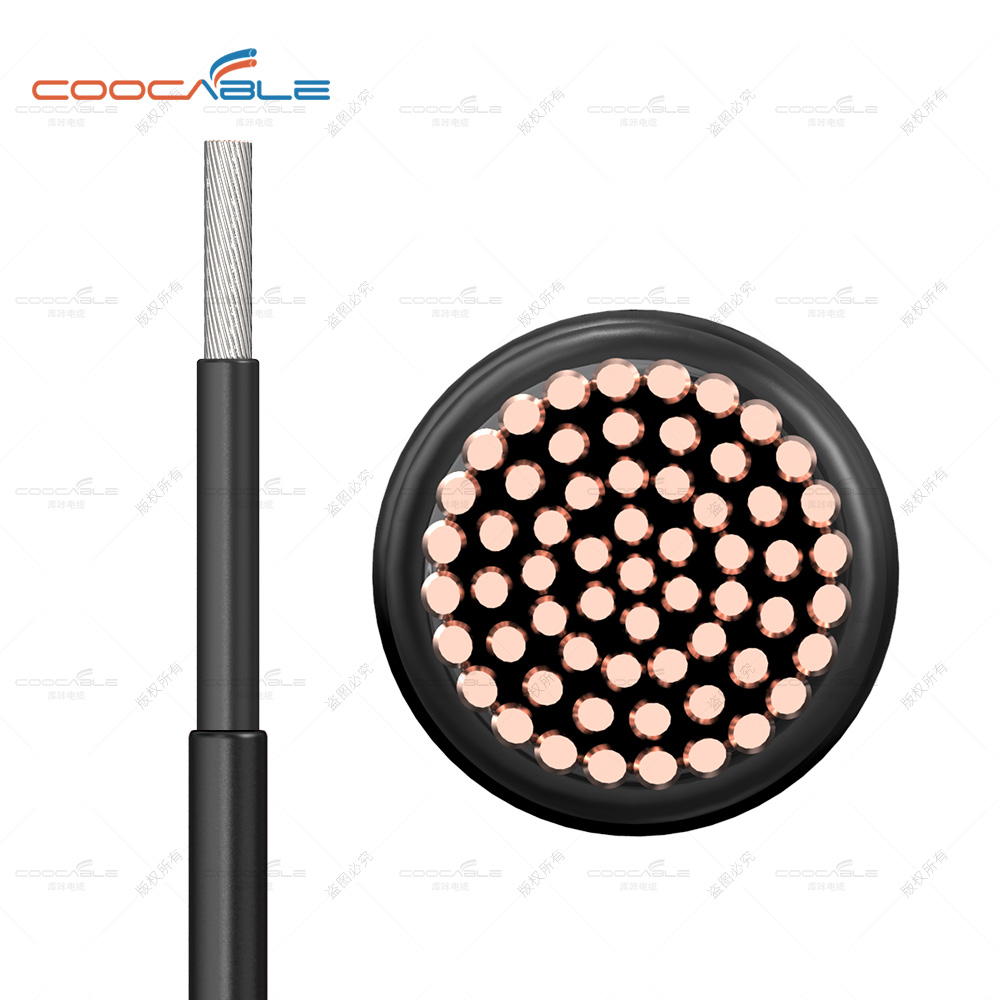
Conductor
Plain annealed stranded circular compacted copper conductor (Class 2).
Conductor Screen
An extruded layer of a cross-linkable semi-conducting compound
as a stress control layer.
Insulation
An extruded layer of cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE).
Insulation Screen
An extruded layer of a cross-linkable semi-conducting
compound firmly bonded to the insulation.
Metallic Screen
Flat plain copper tape helically applied over the insulation
screen with suitable overlap.
Filler
Non-hygroscopic polypropylene filler is suitable for the cable’s operating temperature.
Outer Jacket
An extruded layer of Polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Issues of attention
With the economic development in recent years, the importance of medium-voltage cables has gradually become prominent, and the demand for medium-voltage cables in all walks of life is also increasing. Because of their characteristics, medium-voltage cables have different sizes and types. With special requirements, the structure of medium-voltage cables is much more complicated than that of low-voltage cables. Moreover, the materials and production processes used are different. The insulation layer of medium voltage cables is generally composed of three layers, conductor shielding layer, insulating material, and insulating shielding layer.
And the raw material of medium voltage cables is also different, even though the insulation has the same identification as low voltage cables (eg XLPE), the raw material itself is different to ensure purer insulation. Core identification using colored masterbatches for low-voltage cables is not permitted.
Medium voltage cables also need to pay special attention to the common failure problems in use. Most of the reasons are caused by the aging of the cable infrastructure. Generally, partial discharge is actually a harbinger of failure, because it provides evidence that the cable is beginning to deteriorate. , which will cause malfunctions and failures, and power outages later.
Cable aging typically begins with reducing electrical resistance to affect cable insulation, which is a key indicator of defects including moisture or air pockets, water trees, electrical trees, and other issues. Additionally, the breakaway jacket can be affected by aging, increasing the risk of reaction or corrosion, which can cause problems later in service.