The role of diodes in photovoltaic arrays
The role of diodes in photovoltaic arrays
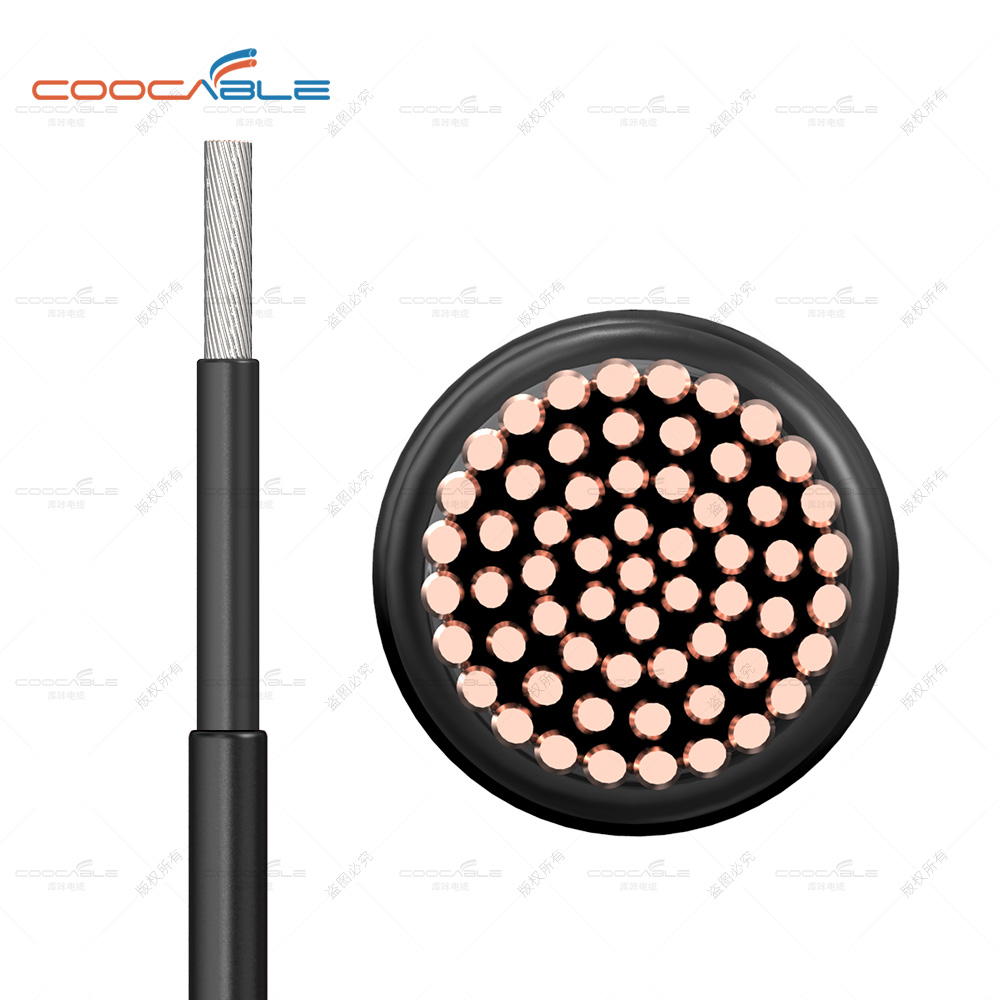
Solar arrays are sensitive to shade. In the silk circuit, each component or part of the battery is blocked from light, which may cause the reverse voltage on the component or battery, which may cause permanent damage to the component in severe cases. Therefore, when arranging the photovoltaic panels in series, it is generally necessary to connect several photovoltaic cell components in series according to the required voltage to form several series, and then connect them in parallel according to the current capacity required by the battery. When photovoltaic cells are connected in parallel, if the light of some cells in a series branch is blocked, it will be used as a load to consume the energy generated by other lighted solar cell strings. The shaded solar cell modules will heat up at this time, which is the hot spot effect. In order to reduce the influence of the hot spot effect, a bypass diode is installed on each photovoltaic cell module in the series circuit, and the shielded solar panel will conduct the current of the entire array through the bypass diode so that the shielded photovoltaic cells do not constitute aload.
A shielding diode, also known as an anti-reverse charging diode, blocking diode, or blocking diode, is connected in series between the energy storage battery or inverter and the photovoltaic array. Its function is to avoid the voltage generated by the photovoltaic cell being lower than the DC bus voltage of its power supply when the solar cell array does not generate electricity or a short-circuit fault occurs in rainy days and nights. The battery plate is damaged due to reverse charging and heating, and the battery's service life is shortened. The shielding diode is connected in series in the solar cell array circuit and plays the role of unidirectional conduction.
Diode Characteristics
The unidirectional conductivity of diodes makes semiconductors used in almost all electronic circuits. Diodes, which play an essential role in many circuits, are one of the earliest semiconductor devices widely used. The tube voltage drop of the diode: the forward voltage drop of the silicon diode (non-emitting type) is 07v, and the forward voltage drop of the germanium tube is 03v. The forward voltage drop of the light-emitting diode varies with different luminous colors.
The voltage and current of the diode are not linear, so when connecting different diodes in parallel, an appropriate resistance should be connected. The crystal diode is a p-n junction formed by a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor, and a space charge layer is formed on both sides of the interface, and a self-built electric field is built. When there is no applied voltage, the diffusion current caused by the difference in carrier concentration on both sides of the p-n junction is equal to the drift current caused by the self-built electric field
in an electrical equilibrium state. When there is a forward voltage bias in the outside world, the mutual suppression of the external electric field and the self-built electric field makes the load. When the direction of the voltage applied to both ends of the non-linear resistor is different, the current flowing through it is completely different. The increase in the diffusion current of the carriers causes a forward current.